The Age-Defying Workout: How Researchers Are Reversing Muscle Aging at the Cellular Level

What if aging was simply a problem waiting for the right solution? Scientists at leading research institutions have shattered conventional wisdom about muscle decline, proving that cellular aging can be reversed through targeted exercise protocols.
Groundbreaking studies reveal that specific workout strategies can literally rewind the genetic clock inside muscle cells, restoring youthful function to tissues decades older. Mayo Clinic researchers documented participants achieving cellular age reversal of up to 30 years through strategic training interventions.
The fountain of youth isn’t found in exotic supplements or expensive treatments but in the precise application of exercise science. From mitochondrial regeneration to genetic reprogramming, each workout becomes an opportunity to activate dormant cellular repair mechanisms.

These discoveries represent more than just fitness improvements; they offer a blueprint for rewriting the aging process itself. Your muscles are waiting for the signal to begin their remarkable transformation back to youthful vitality.
1. The Cellular Clock of Muscle Aging
Our muscles contain tiny power plants called mitochondria that slowly break down as we age. Scientists have discovered that these cellular batteries lose their ability to produce energy efficiently after age 30.
Protein factories inside muscle cells also slow their production, creating weaker and smaller muscle fibers. Meanwhile, cellular waste builds up faster than our natural cleanup systems can handle it. This toxic buildup triggers inflammation and accelerates the aging process throughout muscle tissue.
Damaged cells stop dividing and begin sending harmful signals to healthy neighbors. Eventually, entire muscle groups lose their youthful strength and recovery abilities. Understanding these mechanisms gives researchers clear targets for intervention strategies.
Tips:
- Track your muscle strength monthly to catch early signs of cellular aging
- Focus on compound movements that challenge multiple muscle groups simultaneously
- Prioritize protein intake within 30 minutes after workouts to support cellular repair
2. Breakthrough Discovery: Exercise as Genetic Reprogramming
Mayo Clinic researchers made a stunning discovery in 2017 that changed everything we knew about aging. High intensity interval training can reverse genetic markers of aging by up to 30 years in older adults. Blood samples showed that specific workout protocols actually turn aging genes “off” while activating youth genes.
Muscle biopsies revealed increased expression of genes responsible for energy production and cellular repair. Exercise literally rewrites the genetic instruction manual inside aging muscle cells. This genetic reprogramming happens within weeks of starting targeted training programs.
Different types of exercise influence different genetic pathways, making workout selection crucial. The most dramatic changes occur when combining resistance training with interval cardio.
Tips:
- Alternate between high intensity intervals and moderate steady state cardio weekly
- Include both upper and lower body resistance exercises in each session
- Allow 48 hours recovery between intense training sessions for optimal genetic adaptation
3. The Mitochondrial Renaissance Protocol
Mitochondria respond to exercise stress by multiplying and becoming more efficient. Specific training intensities trigger a process called mitochondrial biogenesis, creating brand new cellular power plants. High intensity intervals force muscle cells to demand more energy than existing mitochondria can supply.
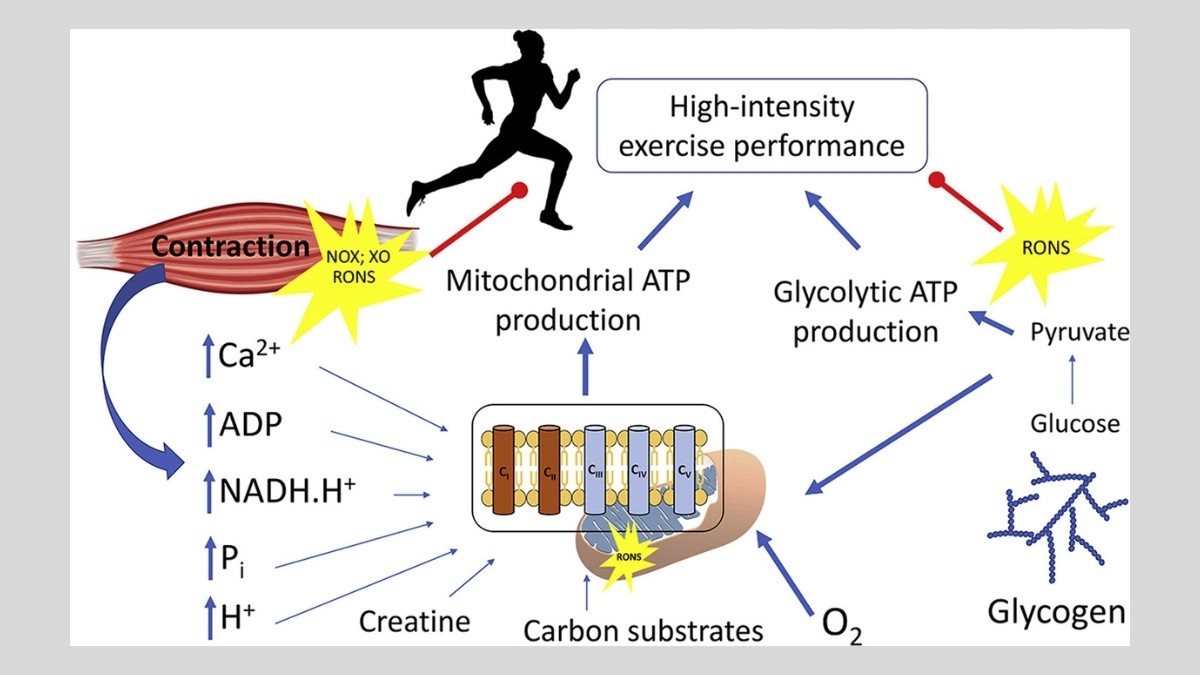
This energy crisis activates genetic switches that command cells to build additional mitochondria. Within 6 weeks, muscle cells can double their mitochondrial density through targeted training. Resistance training also stimulates mitochondrial growth, but through different pathways than cardio.
The combination of both training types creates the most dramatic improvements in cellular energy production. Timing and intensity matter more than duration for triggering mitochondrial renewal.
Tips:
- Perform 4-6 intervals at 85-90% maximum heart rate twice weekly
- Add progressive resistance training 3 times per week with compound movements
- Consume antioxidant rich foods post workout to support mitochondrial recovery
4. Telomeres and Training: The Longevity Connection
Telomeres act like protective caps on the ends of chromosomes, shortening each time cells divide. Regular aerobic exercise can add 9 years of cellular longevity by increasing telomerase enzyme activity.

This protective enzyme rebuilds telomeres, essentially extending the lifespan of muscle cells. Resistance training shows similar but less dramatic effects on telomere preservation.
Athletes consistently show longer telomeres than sedentary individuals of the same chronological age. However, excessive exercise stress can actually accelerate telomere shortening through oxidative damage.
The sweet spot appears to be moderate to vigorous exercise 150-200 minutes per week. Combining different exercise modalities provides the best telomere protection.
Tips:
- Maintain consistent moderate exercise rather than sporadic intense sessions
- Include yoga or stretching to manage exercise induced stress hormones
- Get adequate sleep as poor recovery accelerates telomere shortening
5. Autophagy Activation Through Movement
Autophagy works like a cellular recycling system, breaking down damaged proteins and organelles. Exercise activates this cleanup process within hours of finishing a workout session.

Fasting combined with exercise creates even more powerful autophagy activation. Muscle contractions generate cellular stress that triggers autophagy pathways throughout the body.
This natural detox process removes toxic buildup that would otherwise accelerate aging. Different exercise intensities activate autophagy through separate molecular mechanisms.
Endurance exercise primarily uses energy depletion pathways while resistance training uses mechanical stress signals. The most effective protocols combine both approaches for maximum cellular cleanup.
Tips:
- Exercise in a fasted state 2-3 times weekly to enhance autophagy activation
- Include both steady state and interval training to trigger different cleanup pathways
- Stay hydrated during workouts as dehydration impairs cellular cleanup processes
6. Satellite Cell Awakening: Regeneration Revolution
Satellite cells are muscle stem cells that lie dormant until activated by exercise stress. These cellular repair crews can regenerate damaged muscle tissue and create entirely new muscle fibers. Age typically reduces satellite cell numbers and responsiveness, limiting muscle recovery.
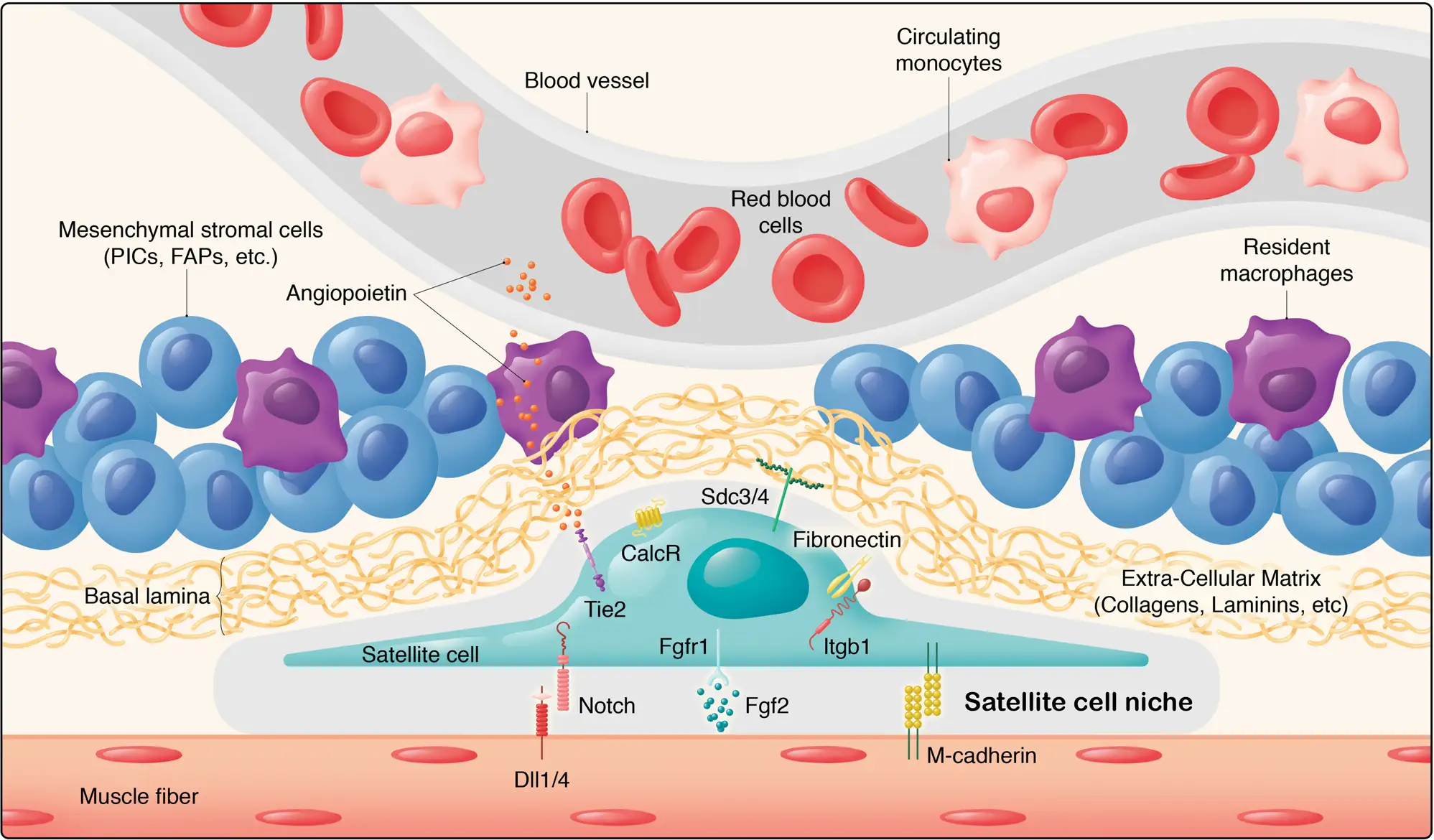
Resistance training provides the mechanical stimulus needed to wake up sleeping satellite cells. Strategic workout programming can restore satellite cell activity to youthful levels within 8-12 weeks.
Proper nutrition, especially leucine rich protein, supports satellite cell activation and proliferation. Recovery periods between workouts allow satellite cells time to complete their regenerative work. Chronic overtraining exhausts satellite cell reserves and impairs long term muscle health.
Tips:
- Progressive overload in resistance training provides optimal satellite cell stimulation
- Consume 25-30g high quality protein within 2 hours post workout
- Schedule complete rest days weekly to allow satellite cell regeneration cycles
7. The Inflammatory Reset Button
Chronic inflammation acts like rust inside aging muscle tissue, destroying healthy cells and blocking repair processes. Strategic exercise protocols can flip inflammation from destructive to healing within 4-6 weeks of consistent training.
Moderate intensity workouts trigger anti-inflammatory molecules called myokines that flood muscle tissue. These exercise-induced compounds neutralize harmful inflammatory signals and promote cellular regeneration.
High intensity sessions initially spike inflammation but create powerful anti-inflammatory rebounds during recovery periods. Overtraining keeps inflammation chronically elevated, accelerating muscle aging instead of reversing it.
The key lies in balancing exercise stress with adequate recovery time. Research shows that people who exercise regularly have inflammation markers 40% lower than sedentary individuals.
Tips:
- Limit high intensity sessions to 2-3 times weekly to prevent chronic inflammation
- Include omega-3 rich foods post workout to support anti-inflammatory responses
- Monitor recovery markers like sleep quality and morning heart rate variability
8. Protein Synthesis Resurrection
Muscle protein synthesis naturally declines by 30% between ages 20 and 70, causing gradual muscle loss. Resistance training can restore protein synthesis rates to youthful levels within 8 weeks of targeted programming.

Heavy lifting sends powerful signals to cellular protein factories, commanding them to ramp up production. Combining resistance exercise with leucine-rich protein creates the strongest stimulus for muscle building.
Training muscles through full ranges of motion triggers maximum protein synthesis responses. Eccentric loading, where muscles lengthen under tension, provides especially potent signals for protein creation.
Timing protein intake around workouts amplifies the synthesis response by up to 50%. Even previously sedentary adults can achieve muscle protein synthesis rates comparable to college athletes.
Tips:
- Perform eccentric-focused movements like slow negatives during lowering phases
- Consume 3-4g leucine within 30 minutes after resistance training sessions
- Train each muscle group 2-3 times weekly for sustained protein synthesis elevation
9. Epigenetic Exercise: Rewriting Your Muscle DNA
Gene expression patterns change dramatically with age, favoring breakdown over repair processes. Specific exercise protocols can modify these genetic switches, activating over 274 genes associated with youthful muscle function.

Endurance training upregulates genes responsible for energy production and oxidative capacity. Resistance training turns on genes that control muscle growth and repair mechanisms. The combination approach creates the most comprehensive genetic reprogramming for age reversal.
These genetic changes occur within days of starting exercise but require weeks to produce visible results. Environmental factors like stress and sleep quality influence how effectively exercise modifies gene expression. Some genetic improvements persist for months after stopping training, while others require ongoing stimulus.
Tips:
- Combine resistance and endurance training weekly for comprehensive genetic activation
- Maintain consistent sleep schedules as poor sleep disrupts exercise-induced genetic changes
- Manage stress through meditation or breathing exercises to optimize genetic responses
10. The Hormonal Harmony Protocol
Growth hormone production drops 14% per decade after age 30, accelerating muscle aging processes. High intensity interval training can increase growth hormone levels by 2000% immediately post workout. This massive hormonal surge triggers widespread cellular repair and regeneration throughout muscle tissue.

Resistance training boosts IGF-1, a powerful anabolic hormone that stimulates muscle protein synthesis. Strategic workout timing around sleep cycles maximizes natural growth hormone release during recovery.
Compound movements like squats and deadlifts create the largest hormonal responses compared to isolated exercises. Recovery nutrition influences hormonal responses, with protein and carbohydrates supporting optimal hormone production. Overtraining suppresses beneficial hormones while elevating stress hormones that accelerate aging.
Tips:
- Schedule intense workouts 4-6 hours before bedtime for optimal growth hormone release
- Focus on compound movements that engage multiple large muscle groups simultaneously
- Avoid excessive training volume as overreaching suppresses anabolic hormone production
11. Real-World Results: Clinical Trial Breakthroughs
University of Birmingham researchers documented 68-year-old cyclists with muscle tissue indistinguishable from 20-year-olds. Participants in Mayo Clinic studies reversed cellular aging markers by an average of 15-20 years through targeted exercise interventions.

Blood analysis showed dramatic improvements in mitochondrial function, inflammation markers, and protein synthesis rates. Muscle biopsies revealed increased satellite cell activity and improved cellular repair mechanisms.
One remarkable case study showed a 74-year-old woman achieving muscle strength levels typical of a 30-year-old after 12 weeks of progressive training. Stanford University trials demonstrated that exercise-induced genetic changes can persist for up to 6 months after training stops.
Japanese research confirmed that Masters athletes maintain cellular age 20-30 years younger than their chronological age. These studies prove that cellular age reversal through exercise is not just possible but reproducible across diverse populations.
Tips:
- Track objective markers like strength, endurance, and recovery times to monitor cellular improvements
- Consider working with exercise physiologists for scientifically-based program design
- Document progress through photos, measurements, and performance benchmarks for motivation
12. Your Personal Age-Reversal Blueprint
Creating an effective muscle age reversal program requires systematic progression and consistent execution. Start with 3 weekly sessions combining 20 minutes of resistance training with 15 minutes of interval cardio.
Begin with bodyweight exercises and gradually add external resistance as strength improves. Schedule high intensity intervals on non-consecutive days to allow complete recovery between sessions.
Progress by increasing weight, repetitions, or intensity by 5-10% weekly while monitoring recovery markers. Include mobility work and stress management techniques to support cellular repair processes.
Track sleep quality, energy levels, and workout performance to ensure optimal adaptation. Most people see measurable improvements in strength and endurance within 4-6 weeks of consistent training.
Tips:
- Begin with 2-3 exercises per muscle group performed 2-3 times weekly
- Increase training demands gradually to prevent overuse injuries and overtraining
- Schedule regular assessment weeks to evaluate progress and adjust programming accordingly
Final Thoughts:
The science is clear: aging at the cellular level is not a fixed destiny but a reversible process through strategic exercise intervention. Researchers have proven that targeted training protocols can literally rewind the cellular clock, restoring youthful function to aging muscle tissue.

From mitochondrial regeneration to genetic reprogramming, exercise acts as the most powerful anti-aging medicine available to humanity. These breakthrough discoveries represent a fundamental shift in how we understand the relationship between movement and longevity.






